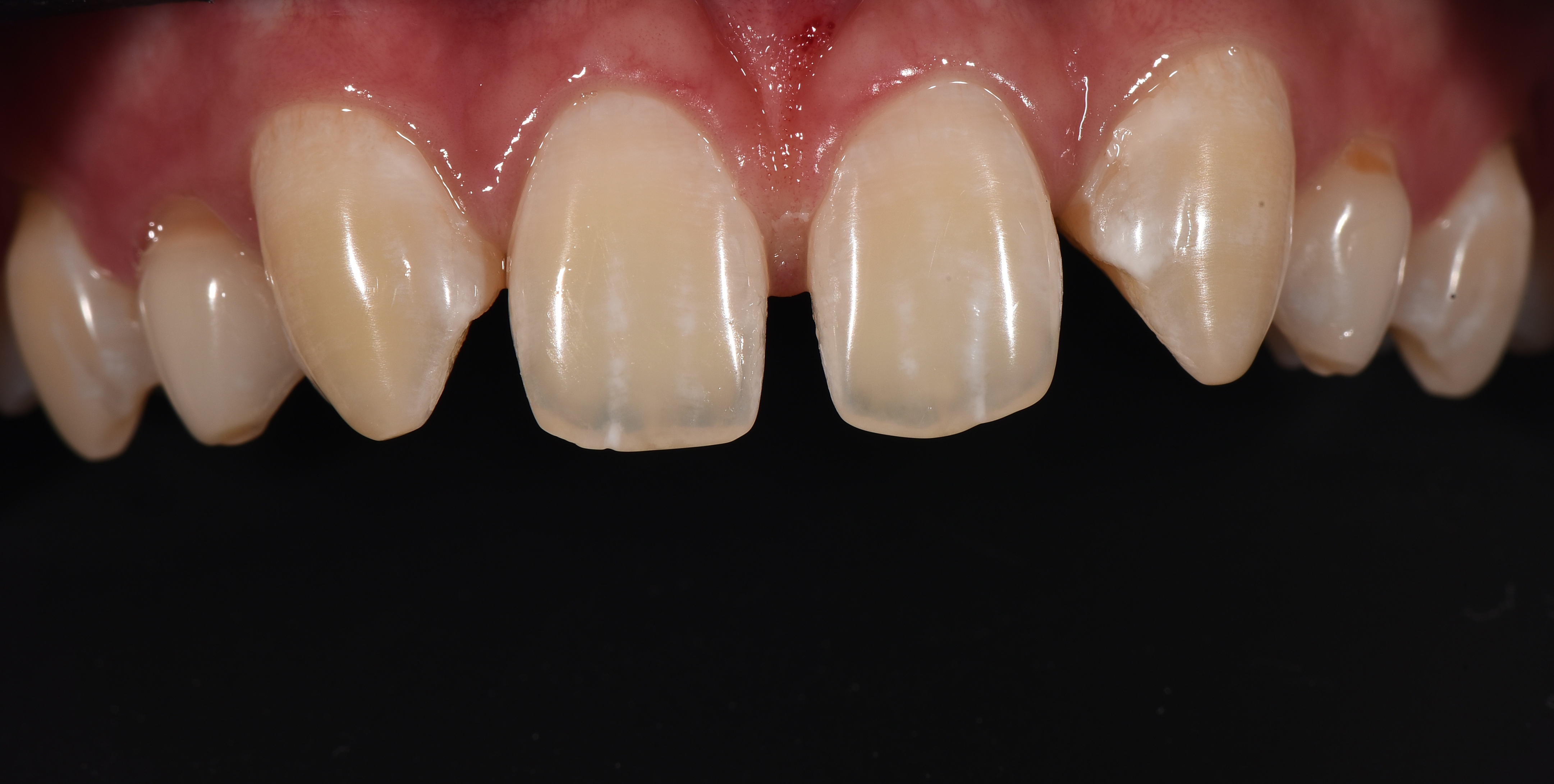
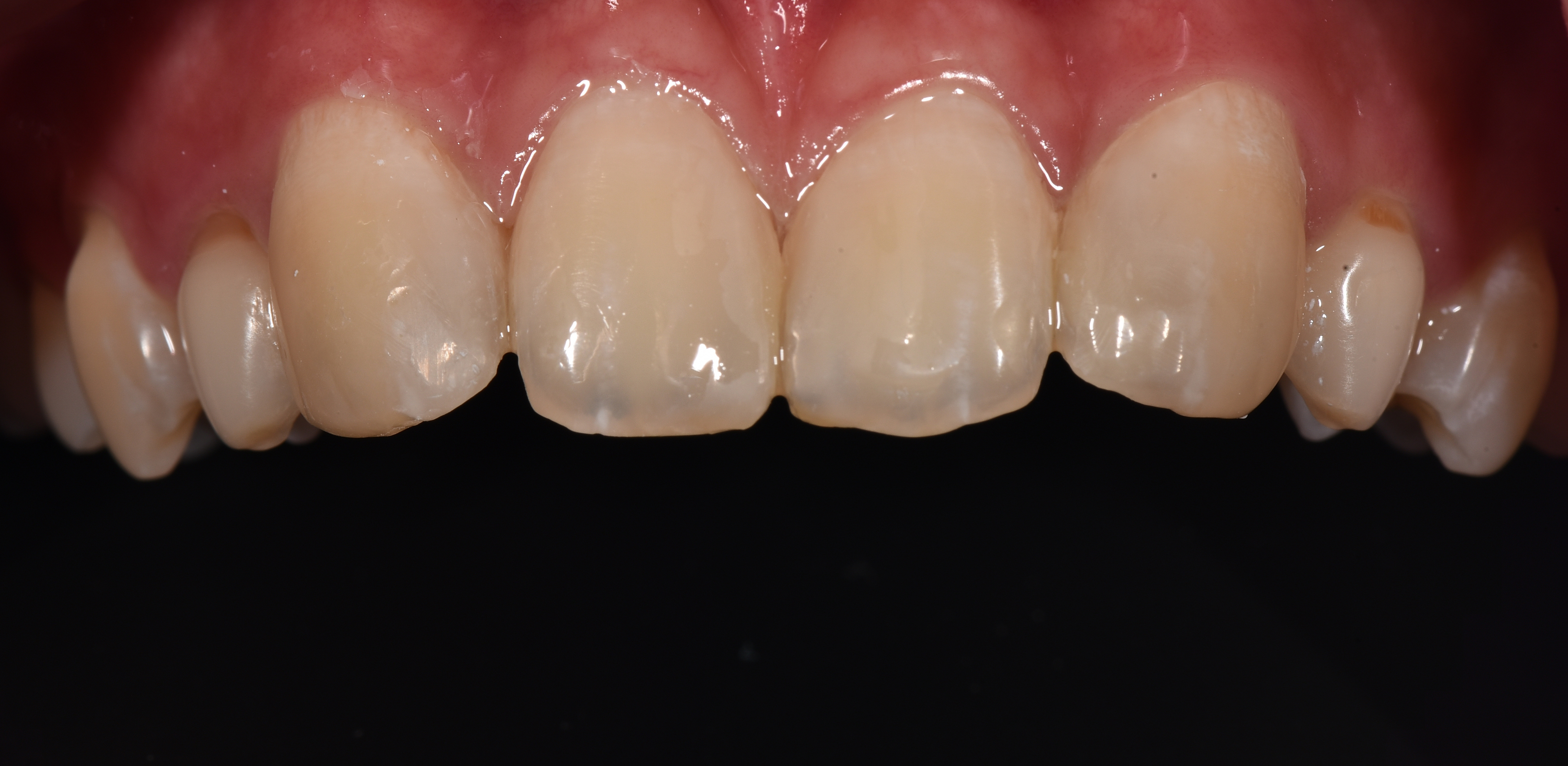
Vote
Voting Period: 06/02/2024 - 13/02/2024 (Extended till 23/02/2024)
Each person can vote THREE entries during the entire voting period,
ONE entry for each category
Select a Category
×
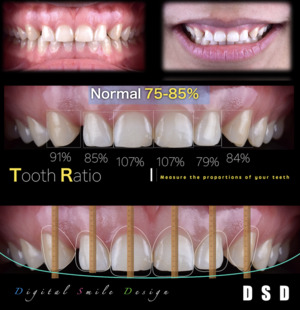
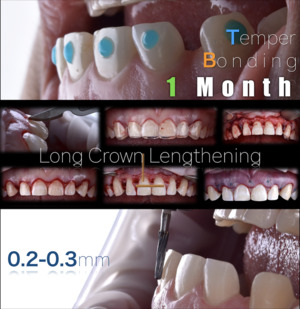
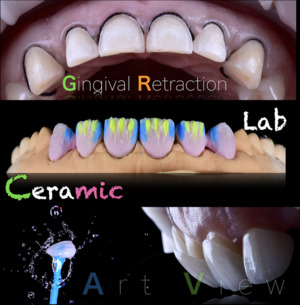
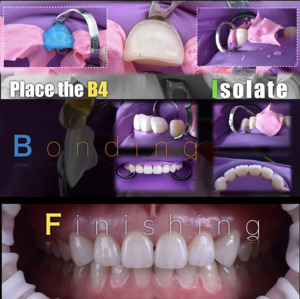
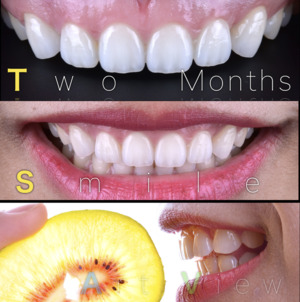





×

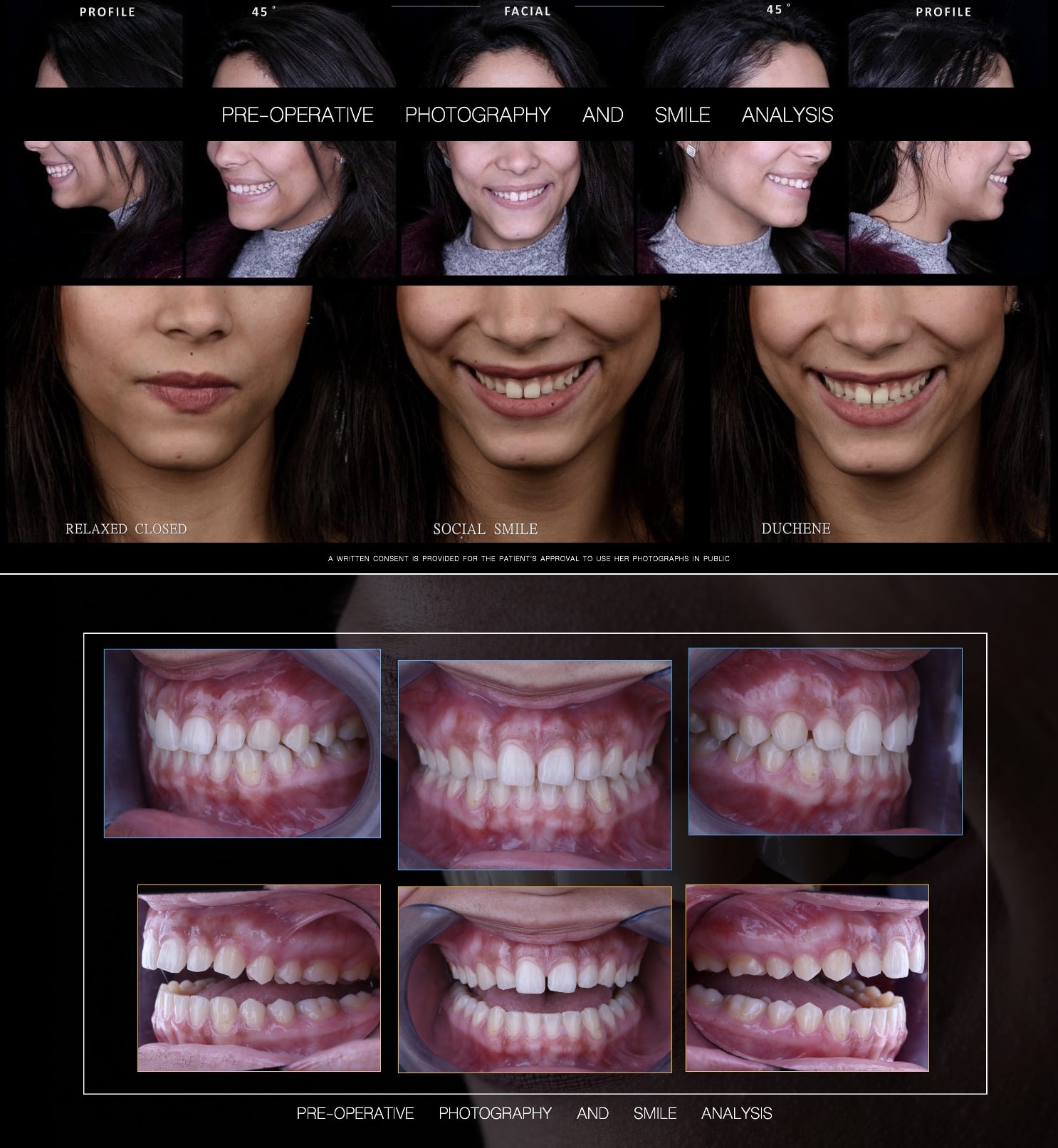
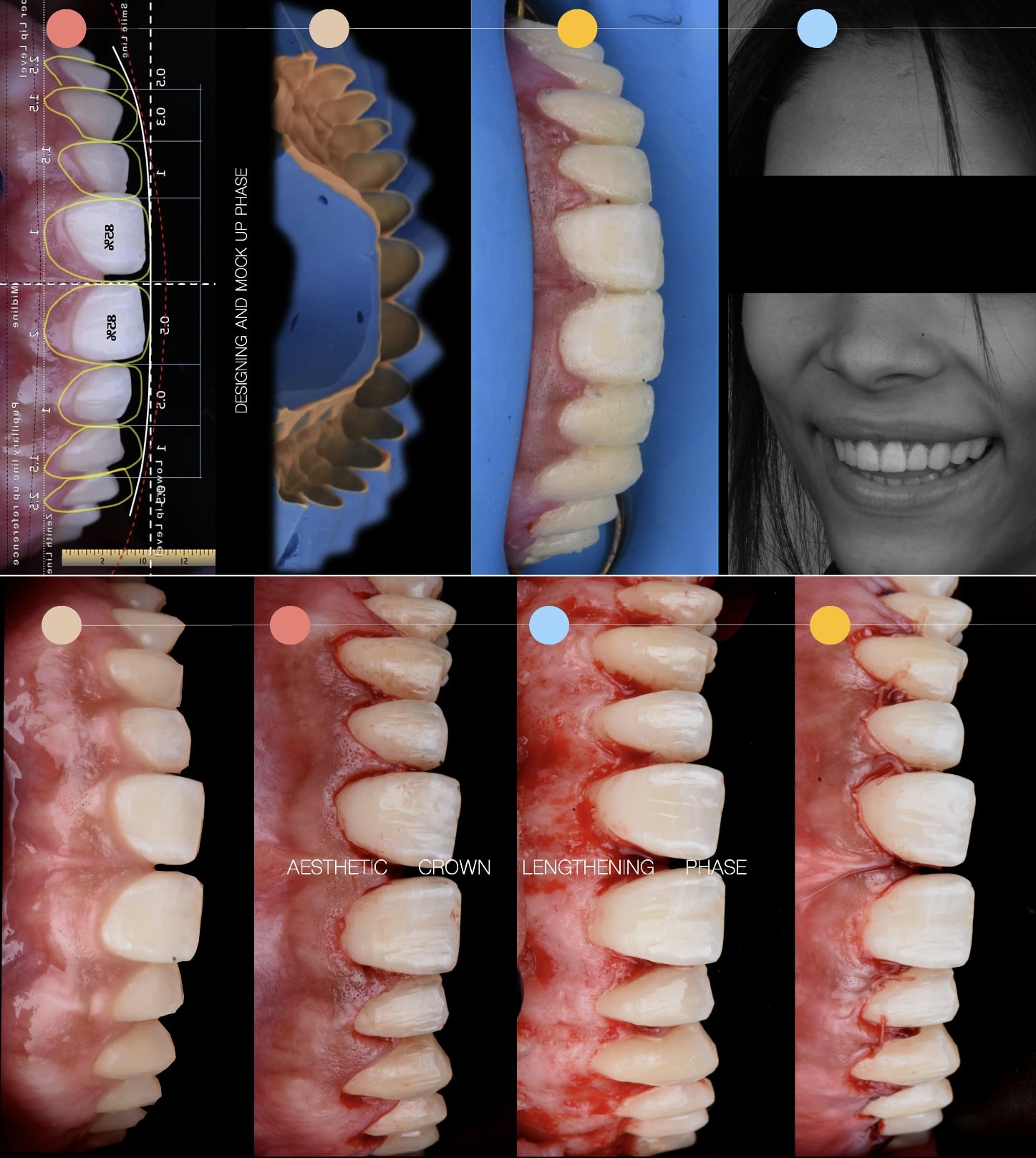
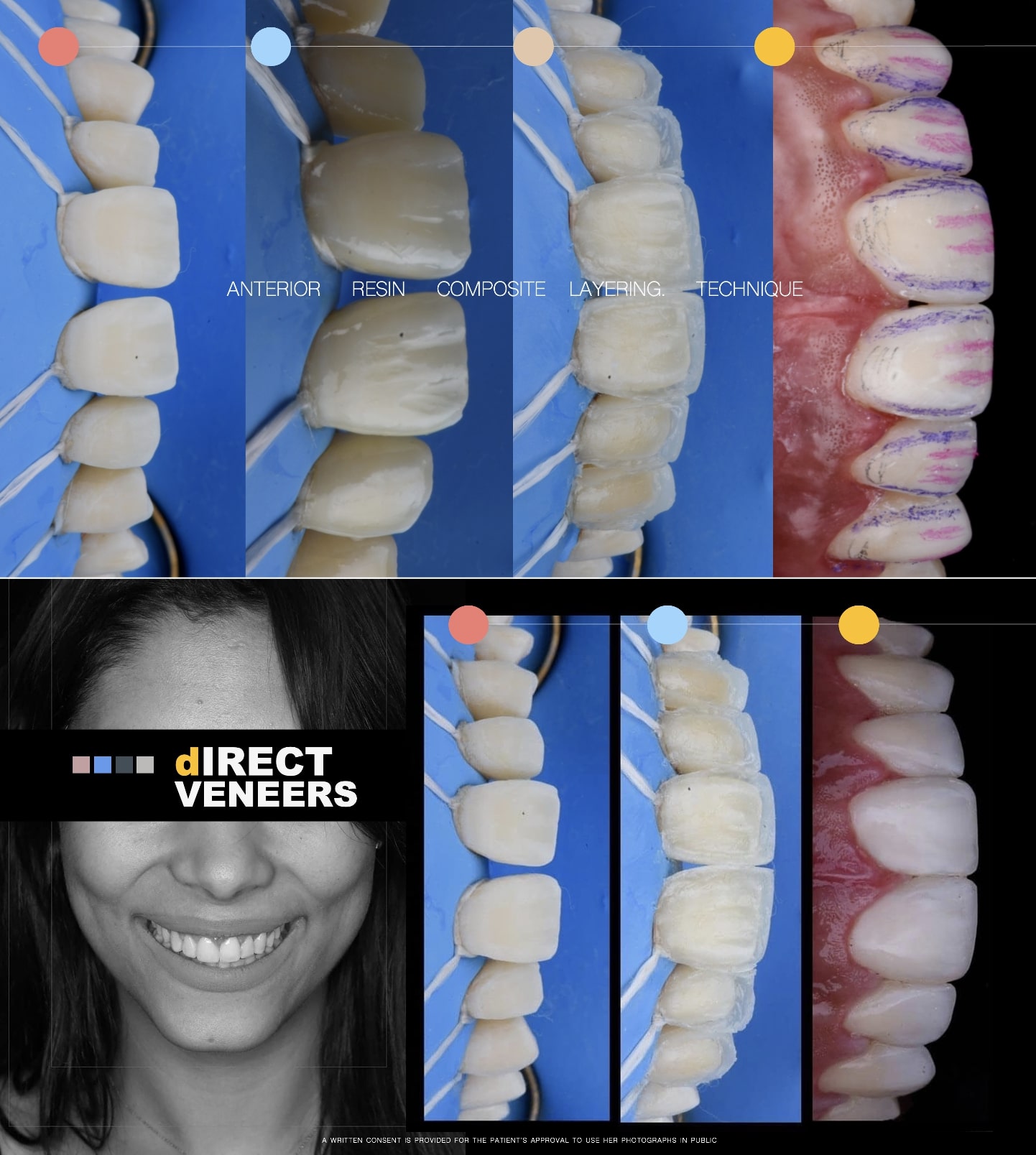
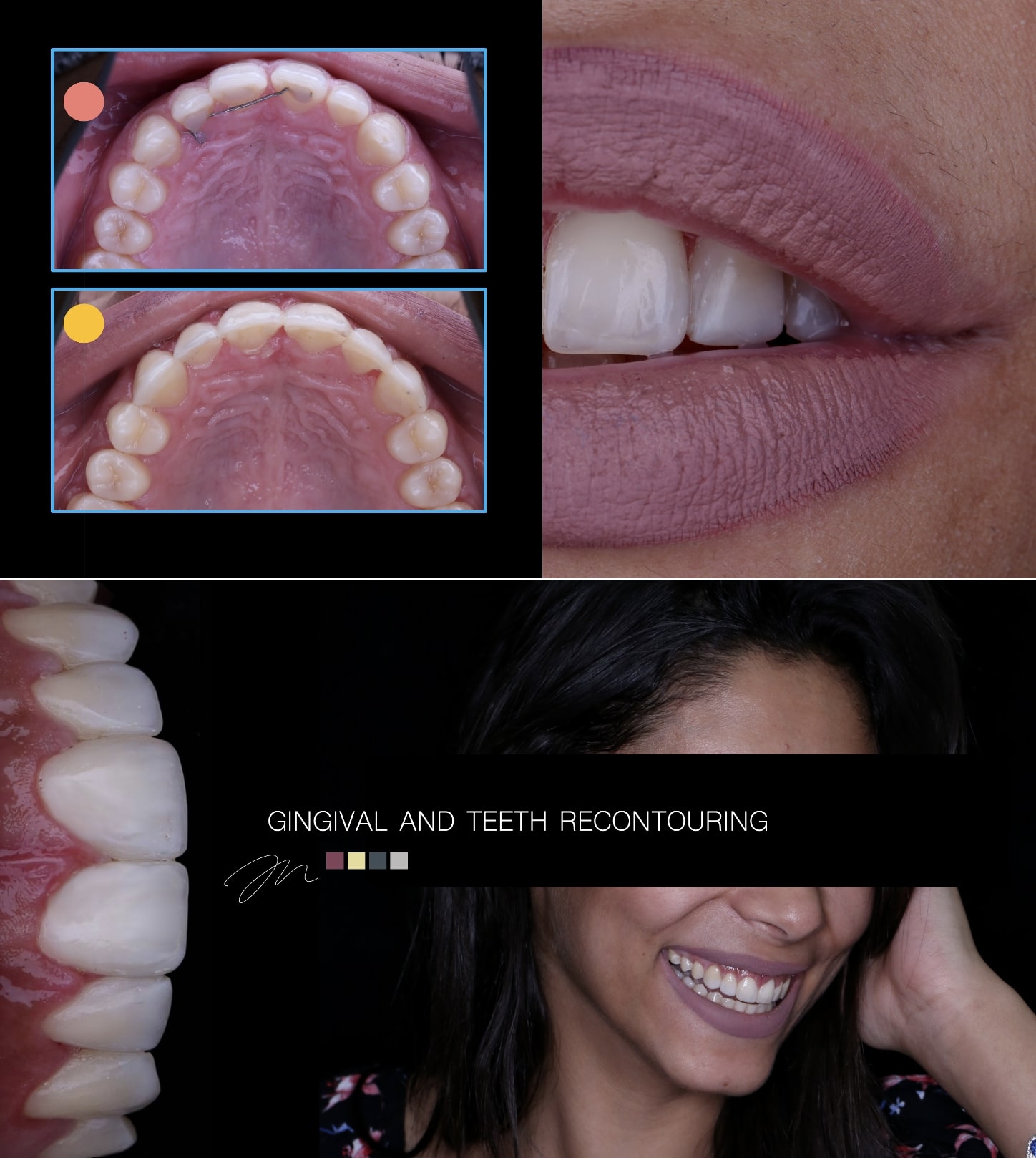





×
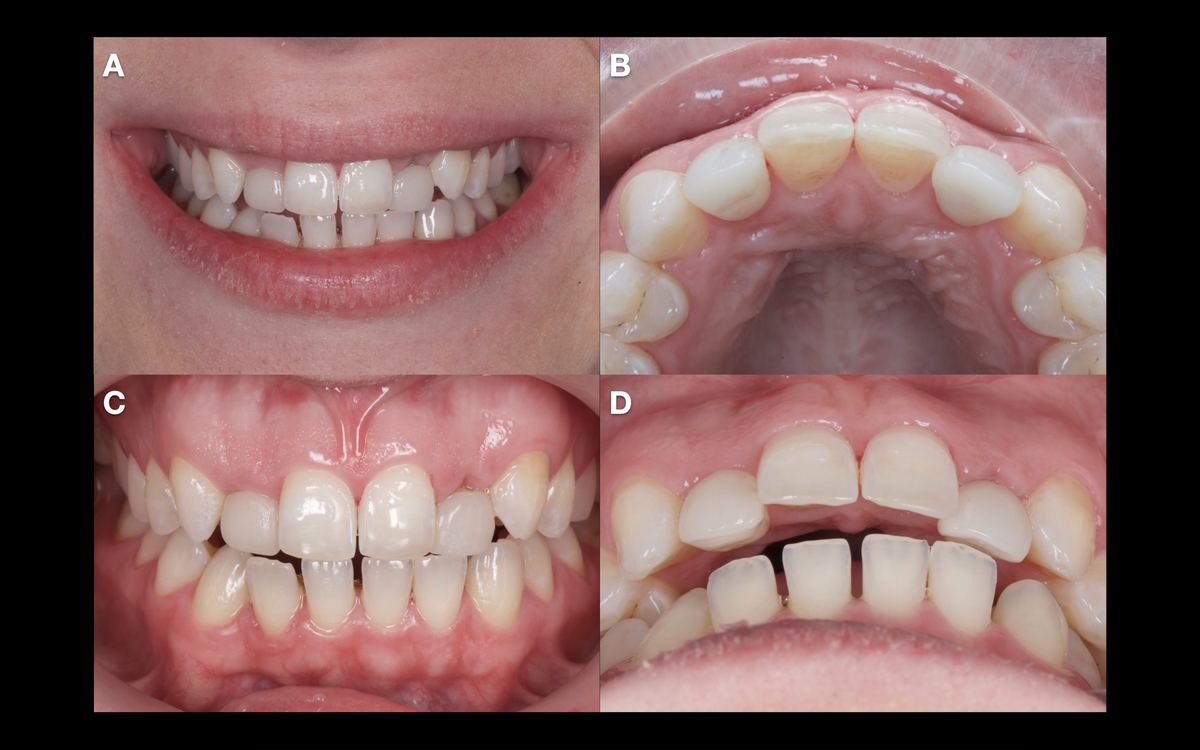
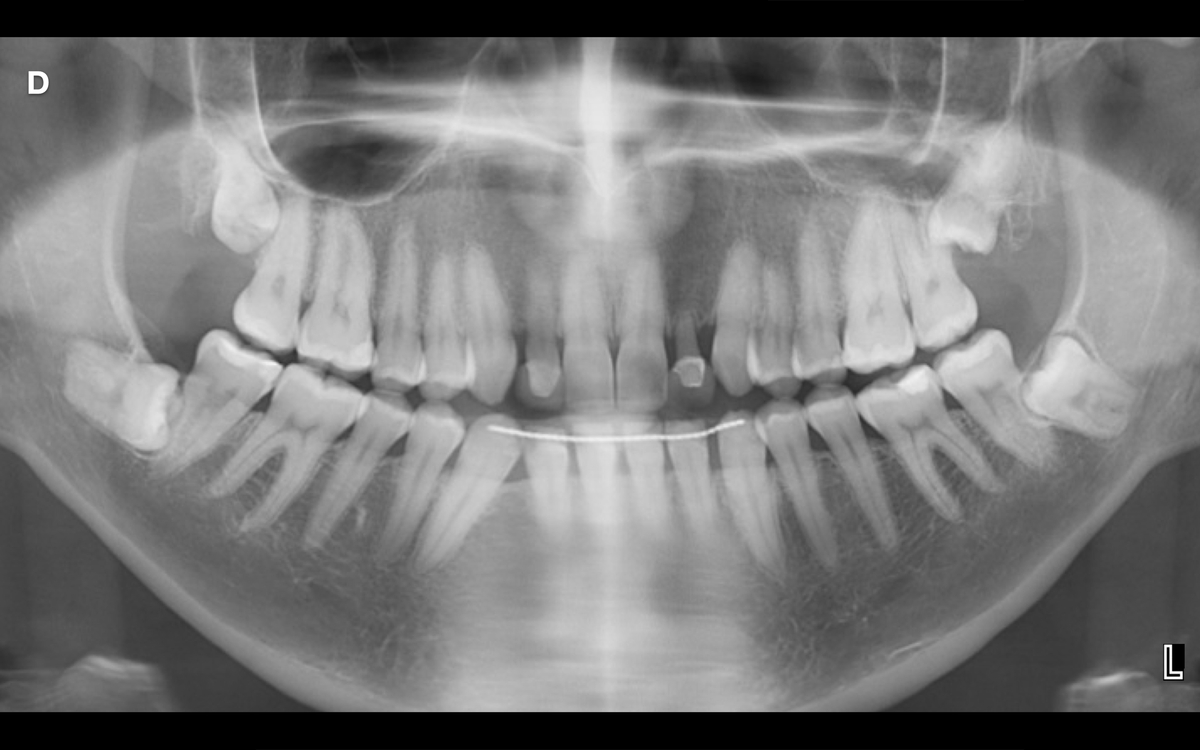
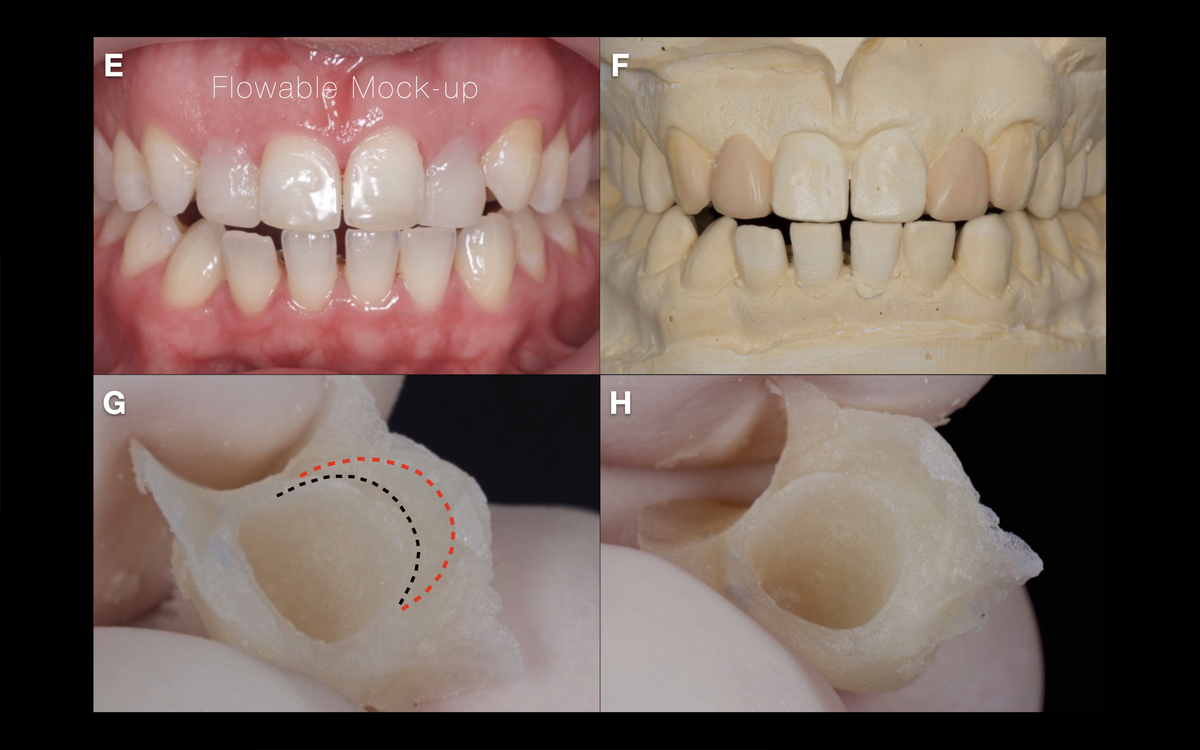
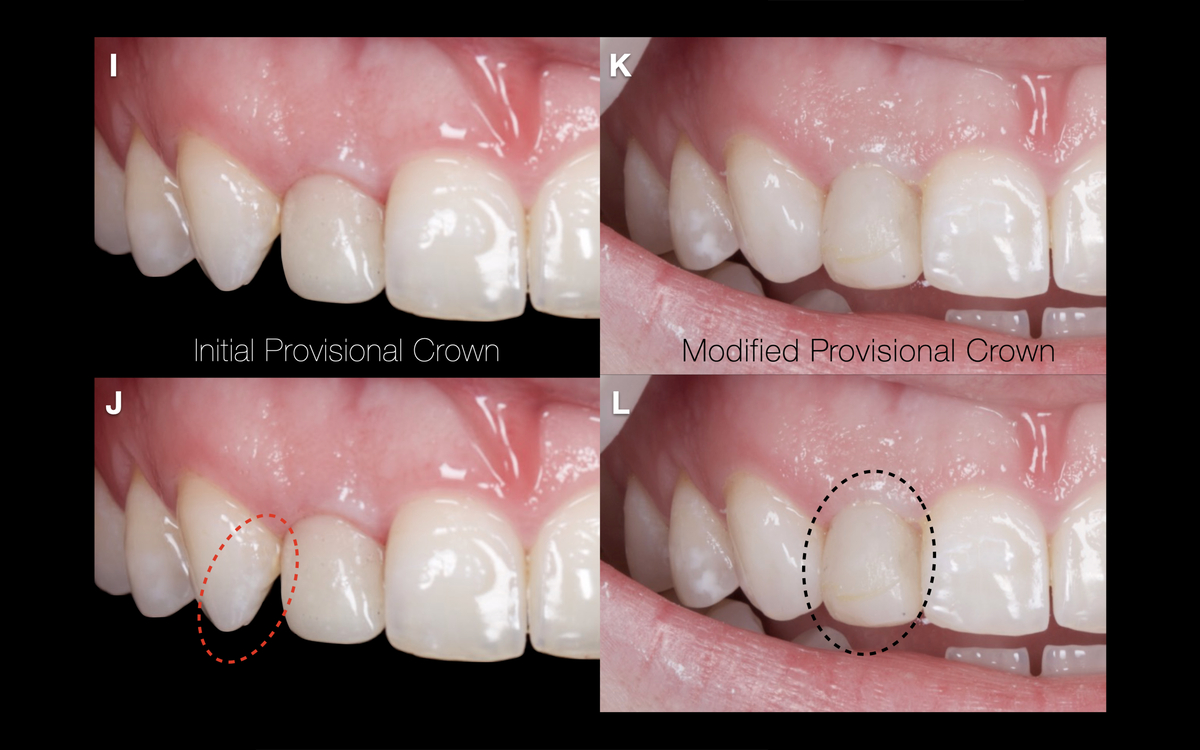
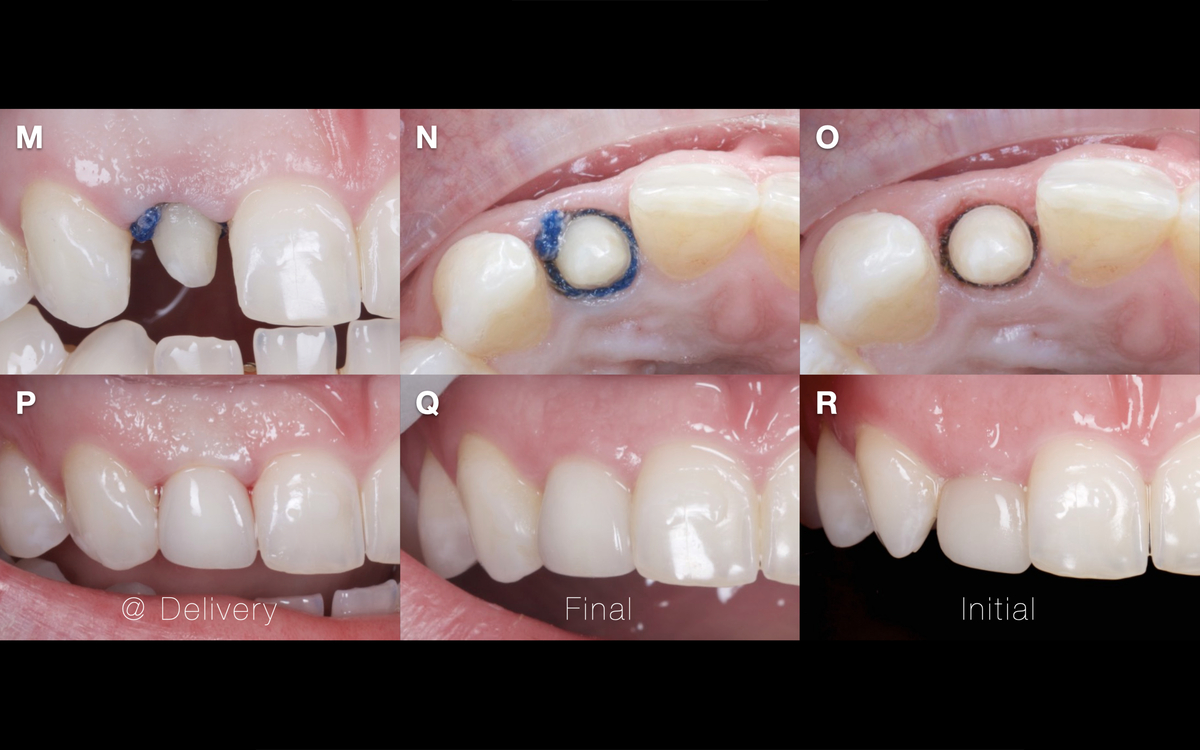





×
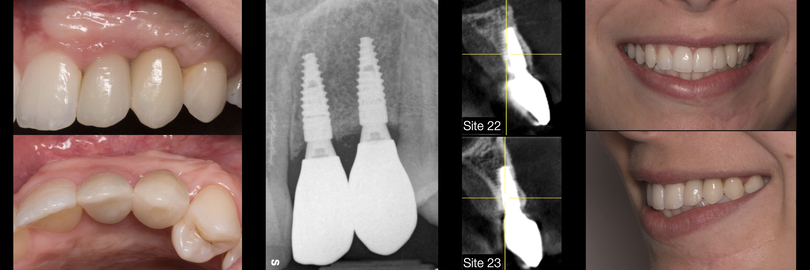





×
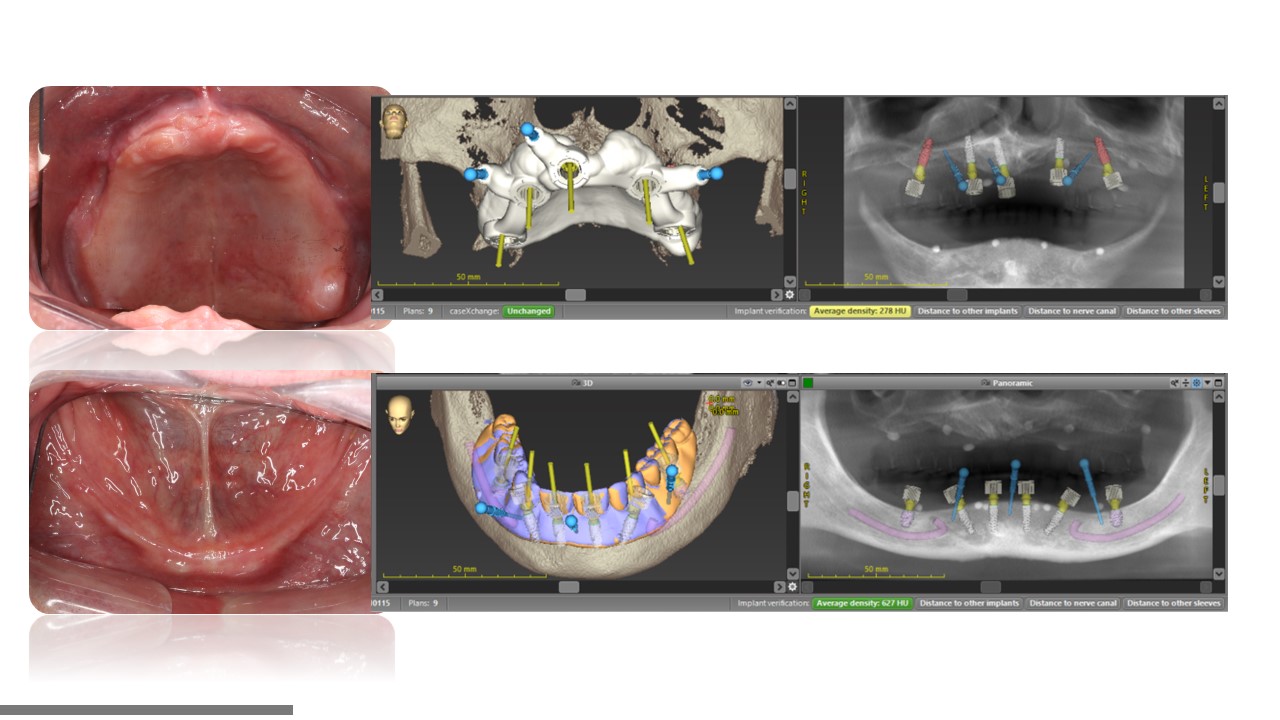
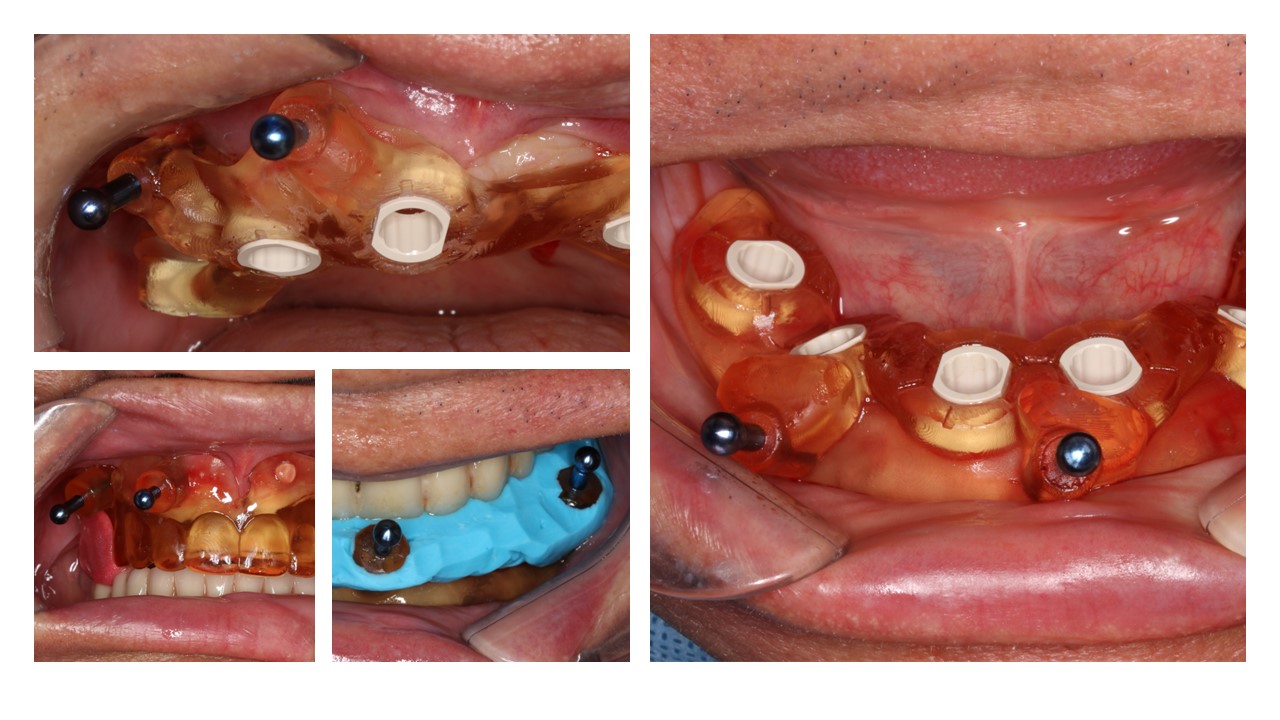
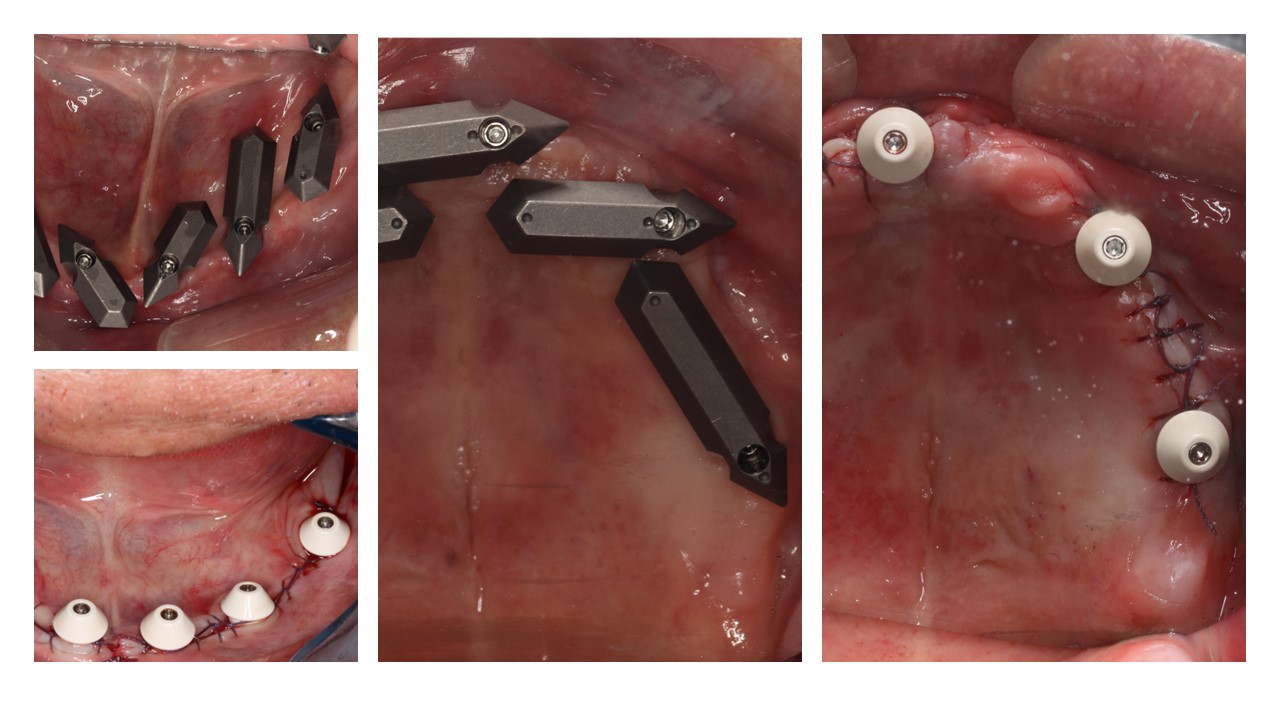
×
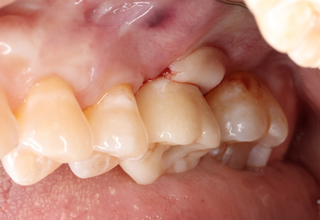
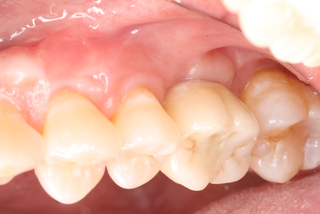
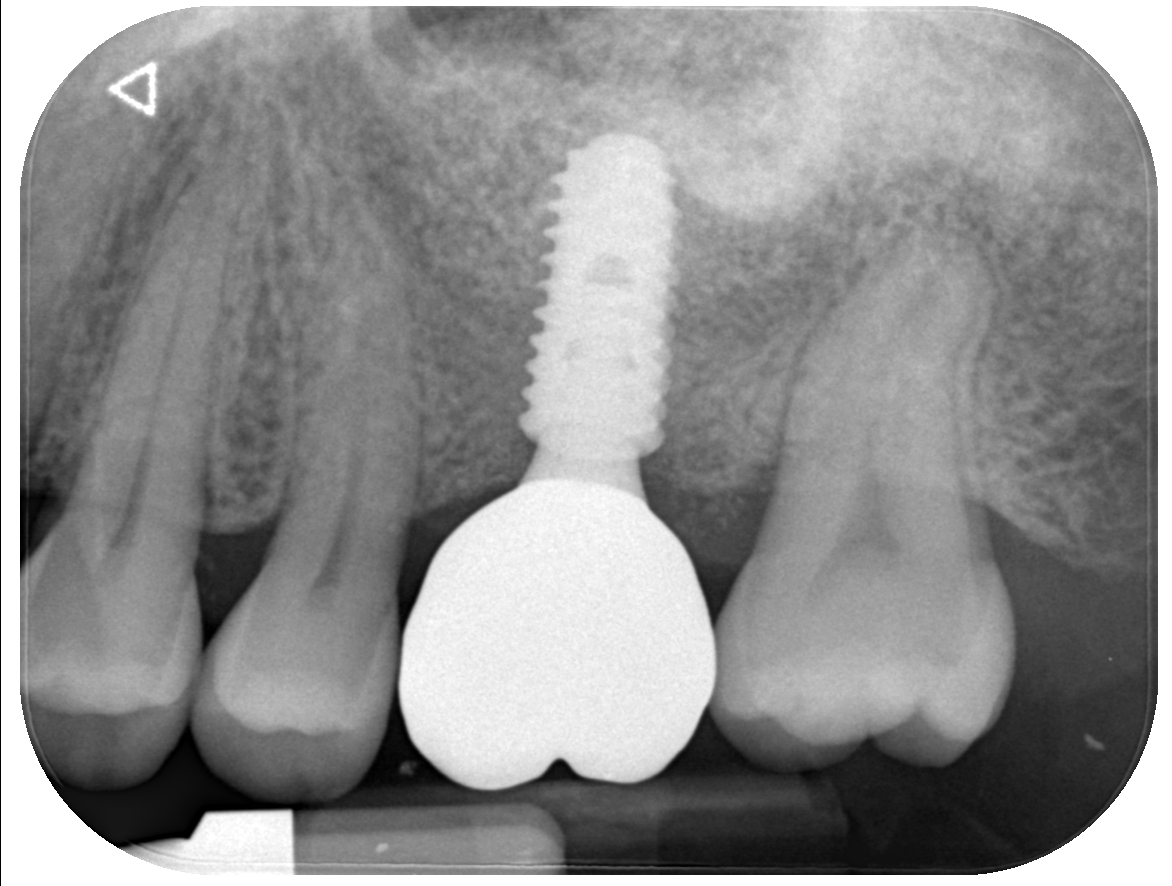





×